UN38.3 is the section of Chapter 38, Paragraph 3 of the United Nations’ “Manual of Tests and Criteria for the Transport of Dangerous Goods.” In 2003, the United Nations adopted a proposal for safety transport standards for lithium batteries led by the United States Department of Transportation (USDOT), officially adding lithium battery products to Section 38, Paragraph 3 of the Orange Book. In 2005, the China International Air Freight Transportation Corporation issued the “Operational Specifications for Transporting Rechargeable Lithium Batteries as Non-Hazardous Goods (Provisional),” as the operational specifications for lithium battery air transport by China Cargo Airlines, and it marked the beginning of the first chapter on lithium batteries UN38.3 in China. The latest version of UN38.3 is the first revision of the sixth edition, ST/SG/AC.10/11/Rev.6/Amend.1.

This standard has been widely accepted by the member states of the United Nations and has been cited by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), and the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to develop their respective battery transportation requirements, becoming the de facto standard for air, maritime, rail, and road transportation globally.
IEC stands for the International Electrotechnical Commission, which includes various standardization organizations. The technical organizations related to lithium-ion batteries mainly include IEC/TC21, IEC/SC21A, IEC/TC35, IEC/TC108, etc. Their specific responsibilities are as follows: IEC/TC21 (Secondary Cells and Batteries Technical Committee) is responsible for all secondary batteries, and specifically for the revision and development of performance and safety standards for lithium-ion battery cells used in electric road vehicles. IEC/SC21A (Alkaline and Other Non-acid Secondary Cells and Batteries Subcommittee) is responsible for the revision and development of all standards for lithium-ion battery cells and battery packs, excluding those used in electric road vehicles, including performance, specifications, and safety standards for lithium-ion battery cells and battery packs used in portable devices, industrial equipment, site vehicles, and UPS. IEC/TC35 (Primary Cells and Batteries Technical Committee) is responsible for establishing standards for primary cells, and together with IEC/SC21A, it is responsible for lithium-ion battery safety transportation standards. IEC/TC108 (Technical Committee on Safety of Electronic Products) is responsible for establishing additional safety requirements related to lithium-ion batteries used in electronic products, such as the flame retardant level of battery pack enclosures and charge-discharge management of host devices. IEC/TC69 (Technical Committee on Electric Road Vehicles and Electric Commercial Vehicles). In 1997, IEC/TC21 and TC69 established three joint working groups, with TC21 leading JWG69Li, which focuses on lithium-ion batteries for automotive use.
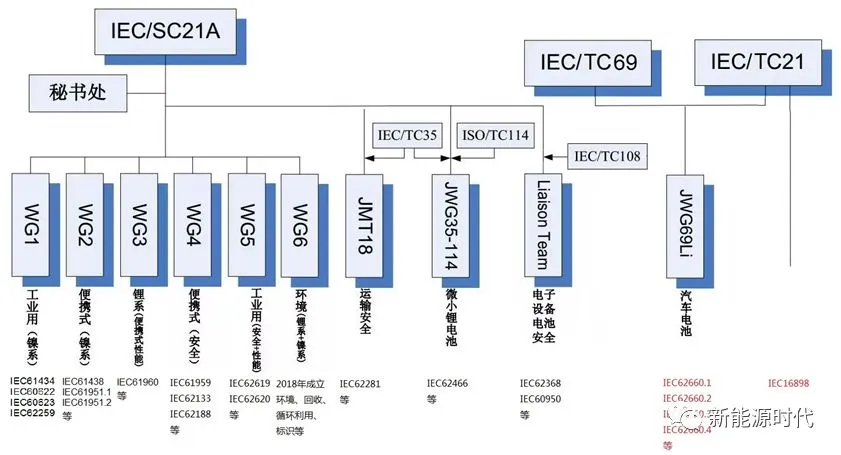
IEC standards related to lithium batteries:
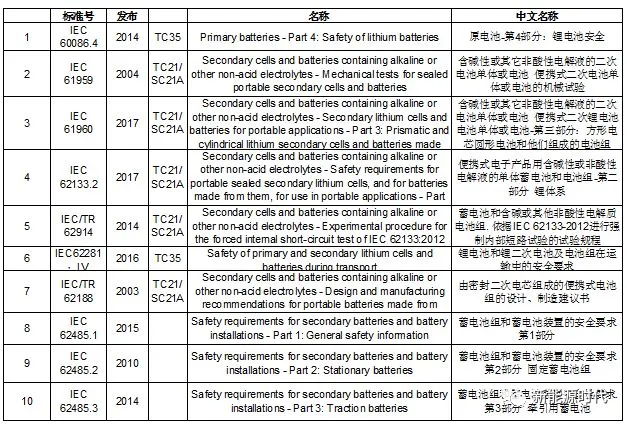
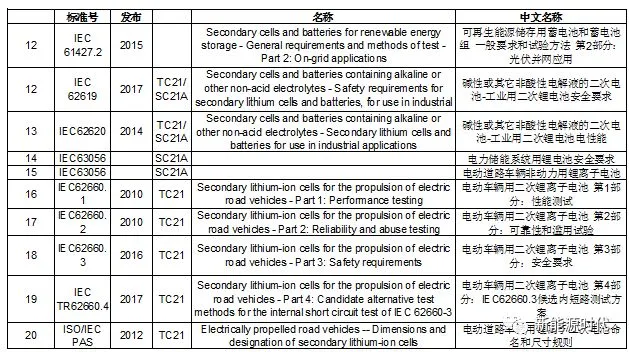
III. ISO
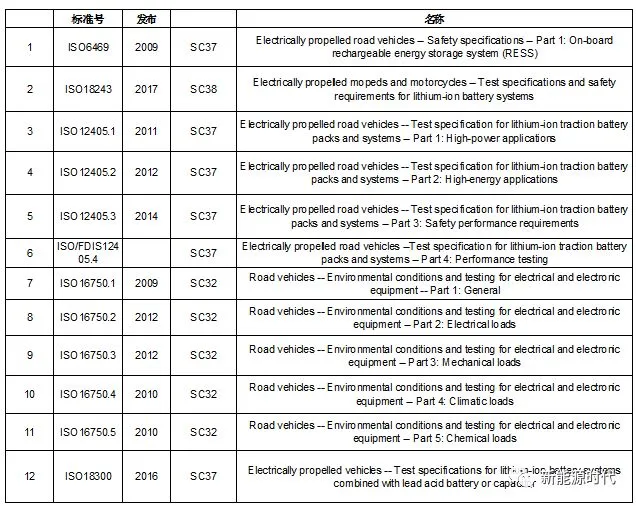
ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO is a Category A advisory organization to the United Nations Economic and Social Council and a Category B (the highest level) advisory organization to the Council for Trade and Development. As a global non-governmental organization, it is currently the largest and most authoritative international standardization body in the world. ISO’s technical work is mainly carried out through its technical committees (TC). TC22 is the designation for the ISO/Technical Committee on Road Vehicles, which has 19 subcommittees (SC), and SC37 is the Subcommittee on Electric Vehicles.
ISO standards related to lithium batteries:
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an international association of electrical and electronic engineers and information science professionals. It is currently the largest non-profit professional technical society in the world, with a presence in over 160 countries. IEEE is dedicated to the development and research in the fields of electrical, electronic, computer engineering, and related sciences. It has established over 900 industry standards in areas such as space, computers, telecommunications, biomedical engineering, power, and consumer electronics, and has evolved into an influential international academic organization. Relevant IEEE standards for lithium batteries:
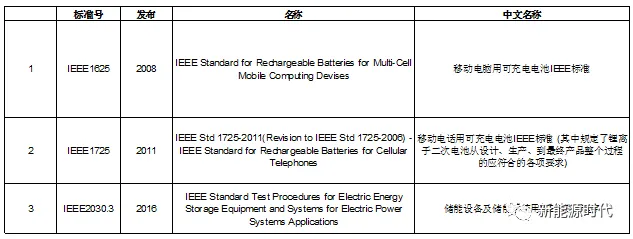
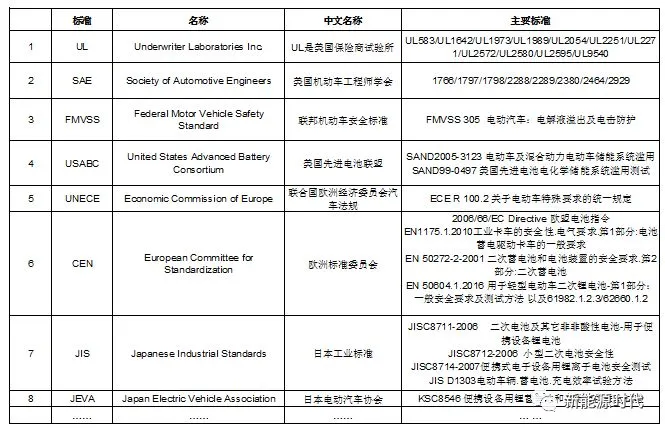
V. Other International Lithium Battery Testing Standards and Organizations
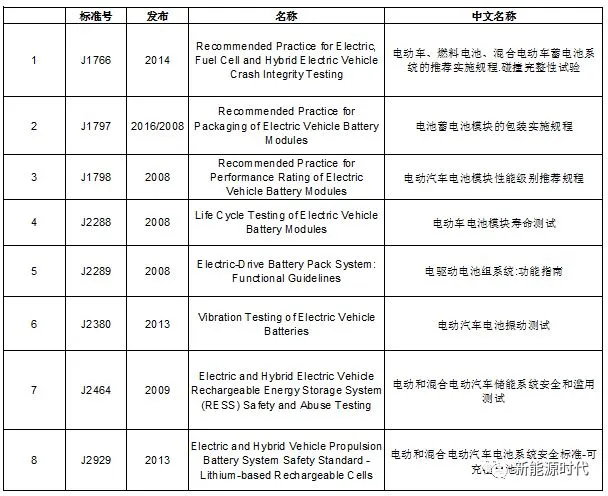
SAE Standards Related to Lithium Batteries:
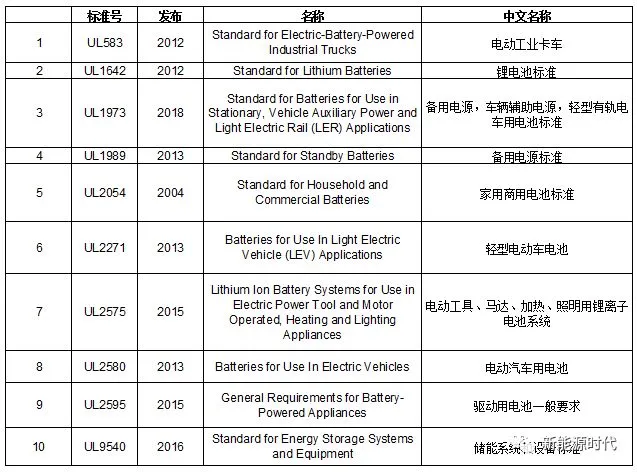
UL Standards related to Lithium Batteries:
From the public account New Energy Era